Makindo Medical Notes.com |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER:The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd | |
Assessing and Painful Red eye
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Episcleritis |Scleritis |Assessing a Red eye |Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma |Allergic and Infective Conjunctivitis |Anterior and Posterior Uveitis |Herpes simplex keratitis (HSK) |Acute Blepharitis |Corneal Abrasion
Intravitreal injections are the modern standard of care for certain types of macular degeneration, diabetic macular oedema and other ophthalmic conditions, and hence are very common. This treatment entails regular injections, sometimes monthly, and prevents blindness in many thousands of patients. It also exposes patients to the rare but devastating complication of intraocular infection (endophthalmitis) following injection. Any patient presenting with ophthalmic symptoms following an intravitreal injection requires urgent ophthalmic review
Acute Red Eye
Acute red eye is a common condition characterized by redness of the eye, which can result from various causes. It often requires prompt evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment. Here is an overview of acute red eye, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and potential complications. Red, painful eye(s) is possibly an Ophthalmological emergency and needs rapid assessment
Causes of Acute Red Eye
- Conjunctivitis:
- Bacterial: Often accompanied by pus and discharge.
- Viral: Associated with watery discharge and often spreads in communities.
- Allergic: Characterized by itching, redness, and swelling, often with clear discharge.
- Corneal Abrasion:
- Scratch or injury to the cornea, causing redness, pain, and tearing.
- Foreign Body:
- Presence of a foreign object in the eye, causing irritation, redness, and tearing.
- Uveitis:
- Inflammation of the uvea, causing pain, redness, and sensitivity to light.
- Glaucoma:
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma presents with severe pain, redness, blurred vision, and halos around lights.
- Blepharitis:
- Inflammation of the eyelids, often causing redness, itching, and flaking at the eyelid margins.
- Dry Eye Syndrome:
- Inadequate tear production leading to dryness, irritation, and redness.
Symptoms of Acute Red Eye
- Redness of the eye.
- Pain or discomfort in the eye.
- Watery, pus-like, or mucous discharge.
- Itching or burning sensation.
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia).
- Blurred vision or decreased visual acuity.
- Feeling of a foreign body in the eye.
Diagnosis of Acute Red Eye
- Clinical Examination:
- Comprehensive eye examination by an ophthalmologist or optometrist.
- Assessment of visual acuity and intraocular pressure.
- Slit-lamp examination to inspect the cornea, conjunctiva, and anterior chamber.
- History Taking:
- Detailed history to identify potential causes and associated symptoms.
- Special Tests:
- Fluorescein staining to detect corneal abrasions or ulcers.
- Swab or culture of discharge for microbial analysis in cases of suspected infection.
- Imaging Studies:
- CT or MRI scans in severe or unexplained cases to rule out deeper eye or orbital involvement.
Complications of Untreated Acute Red Eye
- Corneal ulcers or scarring, leading to vision impairment.
- Chronic or recurrent infections.
- Permanent damage to the eye structures and loss of vision.
Prevention and Management
- Maintaining good eye hygiene to prevent infections.
- Using protective eyewear during activities that could result in eye injury.
- Avoiding known allergens and managing environmental factors.
- Regular eye check-ups, especially for individuals with chronic eye conditions or risk factors.
Causes
- Acute angle closure crisis
- Corneal infection
- Severe intraocular inflammation, (e.g. iritis) or intraocular infection (endophthalmitis).
- Discharge usually indicates a viral, bacterial or allergic conjunctivitis.
If a chemical injury is suspected, postpone further history-taking or examination and immediately begin irrigation of the eye(s)
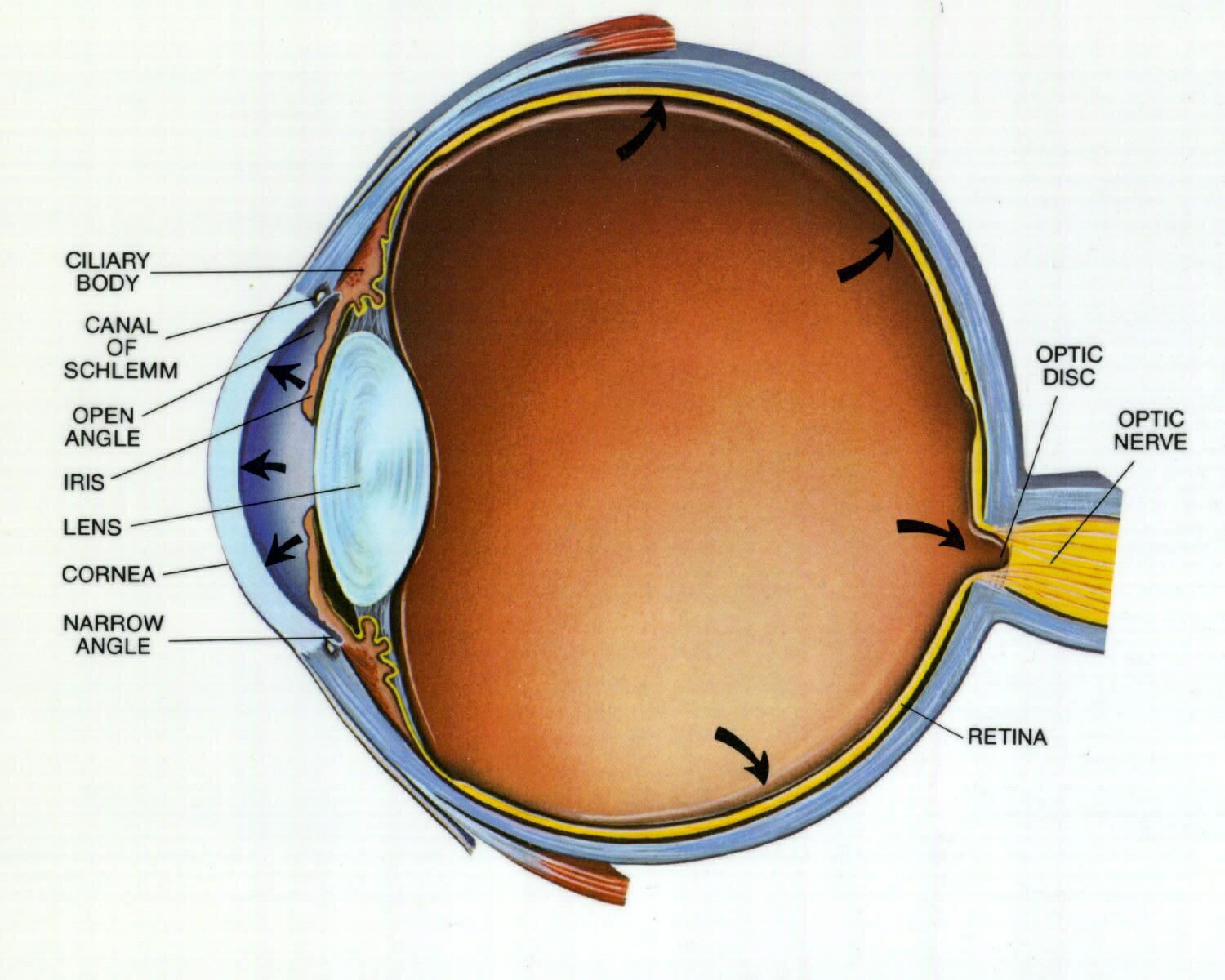
Causes: * need seen same day at eye clinic
Treatment Options for Acute Red Eye
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis:
- Antibiotic eye drops or ointments.
- Maintaining eye hygiene and avoiding contact lens use during treatment.
- Viral Conjunctivitis:
- Supportive care with lubricating eye drops.
- Maintaining eye hygiene and avoiding the spread of infection.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis:
- Antihistamine or anti-inflammatory eye drops.
- Avoiding allergens and using cold compresses for relief.
- Corneal Abrasion:
- Lubricating eye drops and antibiotic prophylaxis.
- Eye patching in some cases to facilitate healing.
- Foreign Body:
- Removal of the foreign object by an eye care professional.
- Lubricating and antibiotic eye drops to prevent infection.
- Uveitis:
- Topical or systemic corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Cycloplegic agents to relieve pain and photophobia.
- Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma:
- Immediate medical treatment to reduce intraocular pressure.
- Laser or surgical procedures to prevent recurrence.
- Blepharitis:
- Eyelid hygiene measures, such as warm compresses and gentle scrubbing.
- Topical antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications in some cases.
- Dry Eye Syndrome:
- Lubricating eye drops and ointments.
- Environmental modifications and dietary changes to improve tear production.