Makindo Medical Notes.com |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER:The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd | |
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) toxicity
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Drug Toxicity - clinical assessment |Metabolic acidosis |Aspirin or Salicylates toxicity |Ethylene glycol toxicity |Ethanol toxicity |Methanol toxicity |Ricin toxicity |Carbon Tetrachloride Toxicity |Renal Tubular Acidosis |Lactic acidosis |Iron Toxicity |Tricyclic Antidepressant Toxicity |Opiate Toxicity |Carbon monoxide Toxicity |Benzodiazepine Toxicity |Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) toxicity |Amphetamine toxicity |Beta Blocker toxicity |Calcium channel blockers toxicity |Cannabis toxicity |Cyanide toxicity |Digoxin Toxicity |Lithium Toxicity |NSAIDS Toxicity |Ecstasy toxicity |Paraquat toxicity |Quinine toxicity |SSRI Toxicity |Theophylline Toxicity |Organophosphate (OP) Toxicity |Toxin elimination by dialysis |Drug Toxicity with Specific Antidotes
Deaths or episodes of acute liver failure in patients who start treatment within 8 hours (h) of a single acute overdose are extremely rare because of the ease of availability of a highly effective antidote, acetylcysteine
About
- A Potentially fatal overdose especially if delayed or non-treatment.
- The minimum lethal dose is usually 24-30 x 500 mg tablets = 12-15 g.
- Determine time taken and amount taken
Metabolism: Toxicity from NADPQI
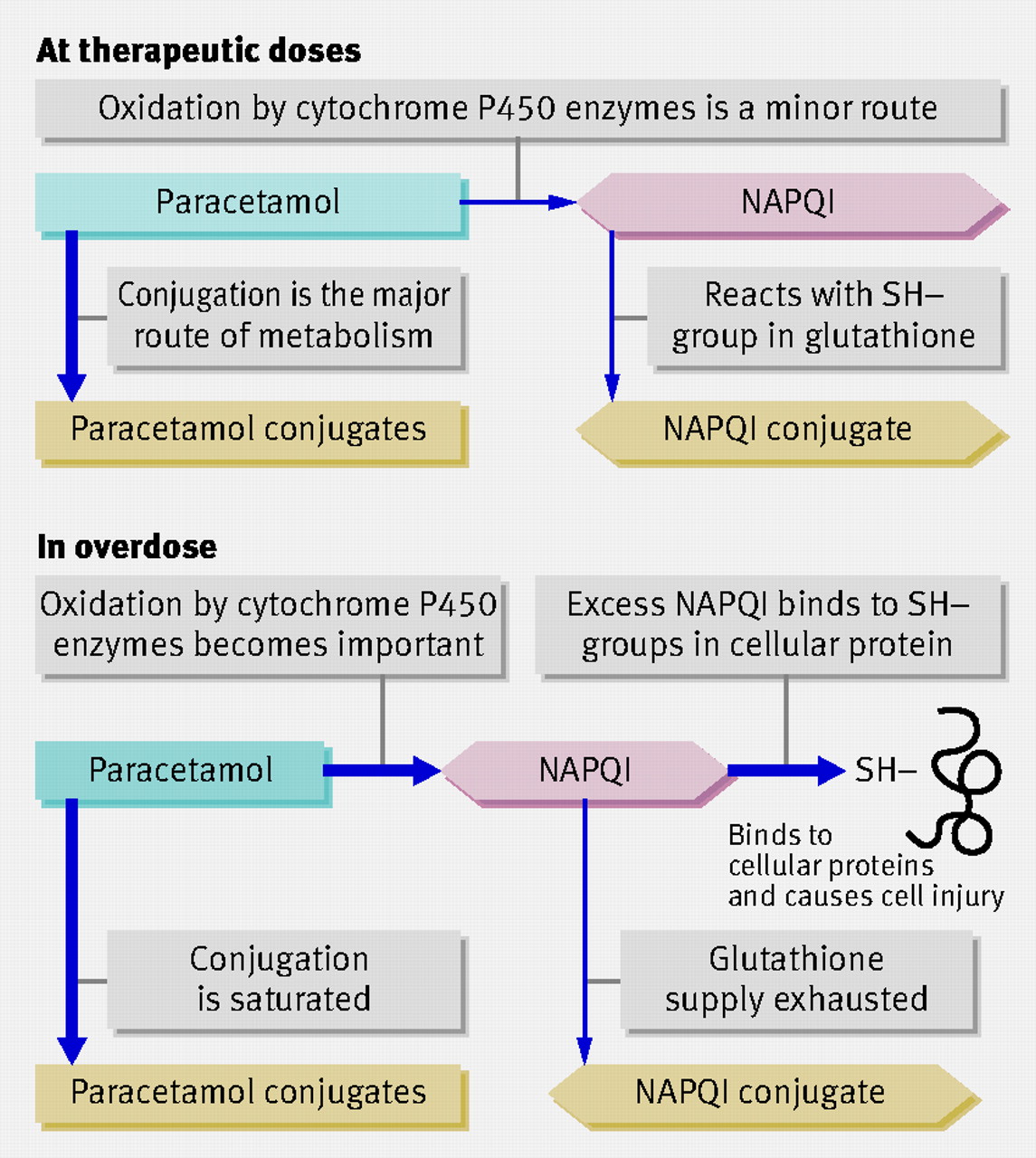
Aetiology
- Paracetamol converted by liver to toxic N-acetyl-p-benzo-quinone imine
- This is usually inactivated by Glutathione which soon is used up in overdose.
- NADQI causes cell damage and hepatic necrosis and liver failure and renal failure too.
Clinical
- Progressive symptoms start 24 hrs post ingestion
- A new distaste for cigarettes suggests liver injury.
- Vomiting and right upper quadrant discomfort
- Bleeding and Hypoglycaemia episodes is a late sign
- Cerebral oedema, encephalopathy, Jaundice
Investigations
- Paracetamol level at 4 hrs post ingestion or later
- FBC, U&E, Salicylate. AST/ALT, Bilirubin, Prothrombin time, VBG
Management: When to start NAC: N-Acetylcysteine
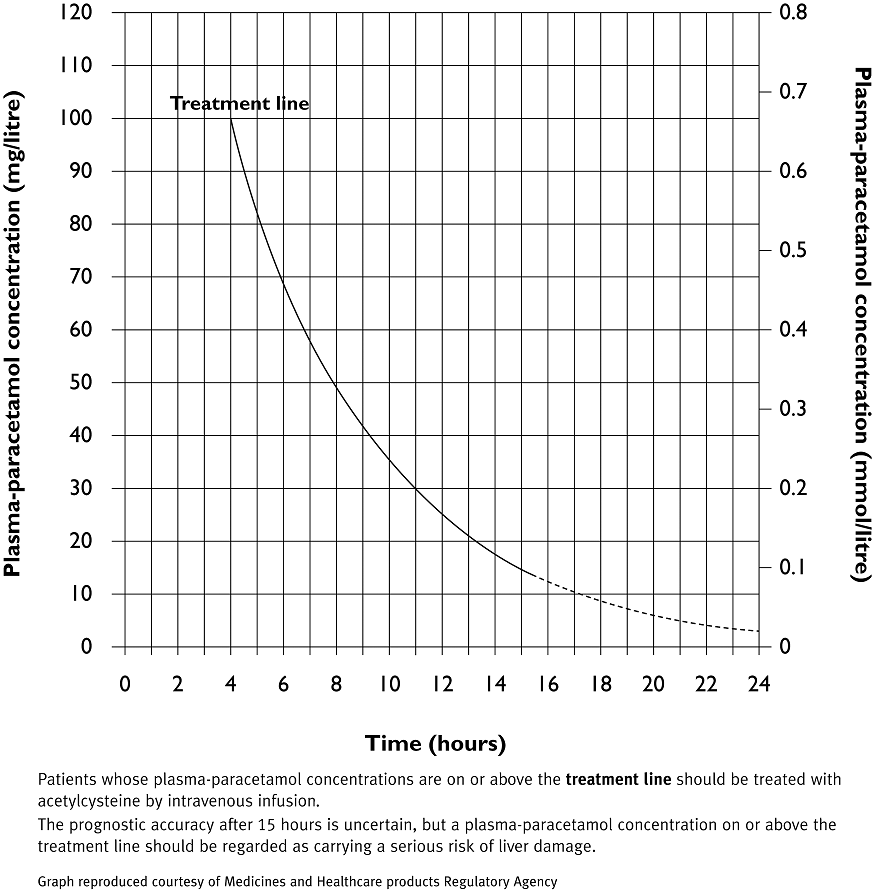
- Those with plasma-paracetamol concentration falls on or above the treatment line on the Paracetamol/Acetaminophen treatment graph
- Who present within 8 hours of ingestion of more than 150 mg/kg of paracetamol if there is going to be a delay of 8 hours or more in obtaining the paracetamol concentration after the overdose
- Who present 8–24 hours after ingestion of an acute overdose of more than 150 mg/kg of paracetamol even if the plasma-paracetamol concentration is not yet available
- Who present more than 24 hours after ingestion of an overdose if they are clearly jaundiced or have hepatic tenderness, their ALT is above the upper limit of normal (unless known elevated before), their INR is greater than 1.3 (in the absence of another cause), or the paracetamol concentration is detectable.
- Consider acetylcysteine treatment in patients who present within 24 hours of an overdose if biochemical tests suggest acute liver injury, even if the plasma paracetamol concentration is below the treatment line on the paracetamol treatment graph
Management: When to give Activated charcoal
- Activated charcoal should be administered (300ml, 50 gm) orally to patients presenting within 1 hour of ingestion and >150 mg/kg ingested.
Treatment line: Treat all above the line
Giving NAC
A ceiling weight of 110 kg should be used when calculating the dose for obese patients. NAC is virtually 100% effective in preventing liver damage when given within 8 hours of the overdose
- Bag 1: NAC: 150 mg/kg in 200 ml D5W or NS over 1 hr
- Bag 2: NAC: 50 mg/kg in 500 ml 5% D5W or NS over 4 hrs
- Bag 3: NAC: 100 mg/kg in 1 L 5% D5W or NS over 16 hrs
- Bag 4: Optional. Give Bag 4 (same as bag 3) if any of the following
- Serum Creatinine elevated above baseline
- Serum ALT elevated 2 x above baseline
- INR >1.3 or a rise in INR of >0.2
Side effects of NAC
- Allergy - rash, Flushing
- Bronchospasm Slow IV Infusion and continue cautiously.
- Ensure access to resuscitation equipment.
- Worsening Please see Liver Transplant for criteria
Monitor
- NEWS, Abdominal pain, Encephalopathy
- Check ALT/AST/Prothrombin time, U&E
- Seek advice if not settling from Liver unit
Criteria for Transfer to Liver Unit
- INR = 3.0
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Hypotension despite fluid resuscitation
- Metabolic acidosis
- Prothrombin time in seconds greater than time since overdose in hours
Poor Prognosis
- Arterial pH = 7.3
- Creatinine = 300 umol/L
- Prothrombin time = 100 seconds
- Grade III/IV Encephalopathy