Makindo Medical Notes.com |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER:The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd | |
Cardiac Examination
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Cardiac Examination |Cardiology History Taking |Respiratory Examination |Gastroenterology Examination |Cardiac Anatomy and Physiology |Coronary Artery Anatomy and Physiology |Cardiac Electrophysiology |Cardiac Embryology
Always ask for the patients permission before beginning the examination.
Wash hands, Introduction and consent
- Examination is an active process and one must be thinking and looking for things not expecting them to just jump out at you.
- Even if you miss a sign or get the diagnosis you may be saved by just talking sensibly and logically about your findings.
- Inspection
- Is the patient comfortable or breathless at rest, anaemic, plethoric, thin, obese
- Is there a GTN spray on locker, IV fluids, IV Nitrates, Inotropes, Insulin
- Mid-sternotomy scar - CABG or valve replacement or correction of congenital heart disease
- Cyanosis suggests > 5g/dl of deoxygenated Hb and if the cyanosis is present centrally may suggest chest disease or a cyanotic heart condition. Sluggish poor circulation can lead to peripheral cyanosis alone with normal central oxygenation.
Face
- Down's syndrome - AV canal defects
- Turner's syndrome - Coarctation of Aorta and Bicuspid Aortic valve
- Mitral facies (malar flush) - suggests Mitral stenosis
- Lips/Mucosa - Central cyanosis
- Eyes - xanthelasma and corneal arcus in a younger person suggests hypercholesterolaemia
- Dentition - potential source of sepsis if rotten (one does not need a dental degree to have a look and comment)
- Thyrotoxic? - AF, signs of Grave's disease with eye and skin signs or a goitre
- Acromegalic - Hypertension and cardiomegaly
- Marfan's syndrome: look in mouth for high arched palate
Hands
- Warm and dilated veins suggest normality or possibly CO₂ retention.
- Cold hands may suggest poor cardiac output or peripheral vascular disease.
- Nicotine staining in a smoker
- Clubbing is an important sign: Other than chest causes consider - Cyanotic congenital heart disease in a young person, Infective endocarditis, Left atrial myxoma
- Splinter haemorrhages - can be a sign of nail trauma in a manual worker or endocarditis. Traumatic lesions are usually seen mainly in the dominant hand. Ask about work done if suspicious
- Osler's nodes - painful lesions in finger pulp suggests endocarditis
- Janeway lesions - Erythematous lesions on palm suggest endocarditis
- Nail fold telangiectasia in those with collagen vascular disease.
- Arachnodactyly "spider fingers" and high arched palate: Marfan's syndrome
- Elasticated skin and joint flexibility: Ehlers-Danlos (Aortic regurgitation)
- Elbow and Achilles tendon: Tendon xanthomata in hands and also elbow and over Achilles tendon suggests hypercholesterolaemia
Pulse
- Feel character and count the rate.
- Assess the rhythm and its regularity or lack of
- Test to see if it is collapsing.
- Compared right radial with left radial and femoral artery looking for delay.
Character
| Pulse characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Good volume | Normal |
| Bounding | High output e.g. post exercise, thyrotoxicosis, fever, Hyperdynamic circulation, severe Paget's disease |
| Collapsing pulse | Aortic regurgitation or AV fistula. Low diastolic pressure. Wide pulse pressure. |
| Plateau pulse | Slow rising small "pulsus parvus" seen with Aortic stenosis. Narrow pulse pressure. |
| Jerky pulse | Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy |
| Pulsus Bisferiens | Mixed collapsing and plateau pulse with mixed aortic valve disease |
| Pulsus alternans | Alternating large and small beats and suggests severe LV dysfunction |
| Pulsus bigeminus | caused by a premature beat before every QRS complex |
| Pulsus paradoxus | Normal BP fall with inspiration is exaggerated > 10 mmHg. Feel pulse weakens with inspiration. Consider Cardiac Tamponade, pericardial constriction and acute severe asthma where inspiration will affect cardiac filling. Pulse weakens during inspiration. |
| Absent | dissection if aorta with ipsilateral subclavian involved, arterial thrombosis or embolism in subclavian or brachial or may be seen post catheterisation (angiography now done via radial artery), Takayasu's disease |
| Radiofemoral delay | Suggests Coarctation of aorta. Be sure to check blood pressure at arm and legif suspicious. |
Rate (normal resting adult 60-90 bpm)
- Bradycardia (Rate < 60): Sinus bradycardia,
- Complete heart block, AV Block 2:1, Atrial flutter or fibrillation with AV block, Sinus arrest with Nodal rhythm
- Tachycardia (Rate > 100): Sinus tachycardia, Supraventricular tachycardia (AVRT, AVNRT), Atrial flutter (Rate = 300 / (2-4)), Atrial fibrillation, Ventricular tachycardia, Ventricular flutter
- Pulseless: Ventricular fibrillation, Ventricular tachycardia, Asystole, Pulseless electrical activity, death.
- If atrial fibrillation should actually count rate at the cardiac apex rather than the pulse as some beats will below the volume and undetectable at the wrist.
Rhythm
| Regular | Sinus Rhythm, Sinus tachycardia, Sinus bradycardia, Atrial flutter with 2:1 or 3:1 block, Complete heart block (slow!) |
| Regularly irregular | Bigemini (normal beat followed by ectopic), Mobitz type II block |
| Irregularly irregular | Atrial fibrillation (commonest abnormality) , SR with multiple ectopics |
Blood pressure
- Arterial pulse waveform is composed of percussion wave travelling along an artery which is at a much higher speed than the actual passage of blood with a dicrotic notch which represents the closure of the aortic valve.
- Blood pressure is measured using a cuff that inflates above systolic pressure occluding arterial blood flow. As the cuff is deflated auscultating over the artery will produce a knocking sound
- Korotkov phase 1 sound which comes on when the cuff is inflated to systolic pressure.
- Korotkov phase 5 signifies diastolic pressure - As the cuff is deflated the sound softens and disappears
- See section on hypertension for more information
Clinical findings
- Hypertension BP > 140/90
- Pulse pressure = systolic - diastolic pressure
- Aortic stenosis - low pulse pressure
- Aortic regurgitation - high pulse pressure
- Right arm pressure > Left-arm pressure by 20 mmHg suggests stenosed left subclavian possibly due to dissection or atheroma
- Left arm pressure > right arm pressure by 20 mmHg suggests stenosed right subclavian possibly due to dissection or atheroma
- Arm (brachial) pressure >>ankle suggests peripheral vascular disease(See ABPI) or it could suggest a Coarctation of the aorta
- Right and left arm pressure often varies by 5-10 mmHg in normals
Praecordium
Listening to murmurs -Traditionally these are the areas but do not really take into account different chest anatomy and physiology and jets of turbulence can be heard outside these areas. Instead of these 4 areas, one can just start in the apex and slide the stethoscope across to the tricuspid area, up the LSE to the pulmonary area and over into the aortic areas listening as you go. A sort of sigmoidal shape. Remember to have one finger on a pulse at all times.
Wash hands, Introduction and consent
Apex beat
- Most inferior and lateral point at which apical beat is palpable. Normally is the 5th ICS in the mid-clavicular line.
- May be difficult to feel if the subject is obese, COPD or pericardial effusion. Feel for the beat and also its character.
- Dextrocardia is very rare but can sometimes appear in exams. There are different types
| Characteristics of Apex beat and chest wall palpation | |
|---|---|
| Forceful Heaving | Aortic Stenosis |
| Thrusting and Dynamic | Aortic regurgitation, Post exercise, Dynamic circulation |
| Impalpable | Pericardial effusion, Emphysema, Obesity |
| Tapping | produced by the mitral valve slamming shut in Mitral Stenosis " palpable S1" |
| Dyskinetic asynchronous | Ventricular aneurysm. Place palm of hand flat on chest and feel a sort of rocking sensation |
| Impalpable | obesity, emphysema and barrel chested, pericardial effusion, dextrocardia |
| Double pulsations | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| Right ventricular heave | Place palm of hand over left sternal edge and see if one can feel the RV lift which suggests RV Hypertrophy. Consider RV to reflect RV dynamics as apex does for the LV apex beat. |
| Thrills "Palpable murmurs" | Place flat of hand across praecordium and see if one can feel any abnormal pulsations or thrills. Time them with pulse. |
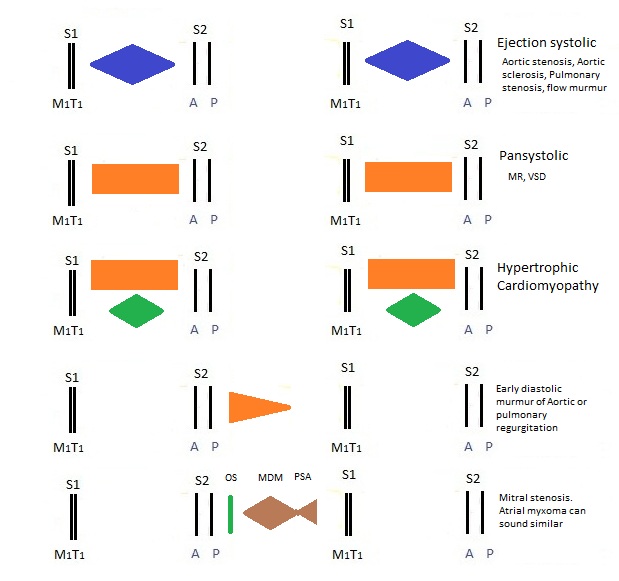
Auscultation
- Listen and time all sound with a finger on a pulse
- Listen in all 4 valve places at least. Listen to axilla and along LSE
- Suspect Mitral stenosis - roll patient on the left side and listen just medial to apex - exercise patient if needed
- For Aortic regurgitation sit patient forward and ask them to exhale slowly and listen the LSE
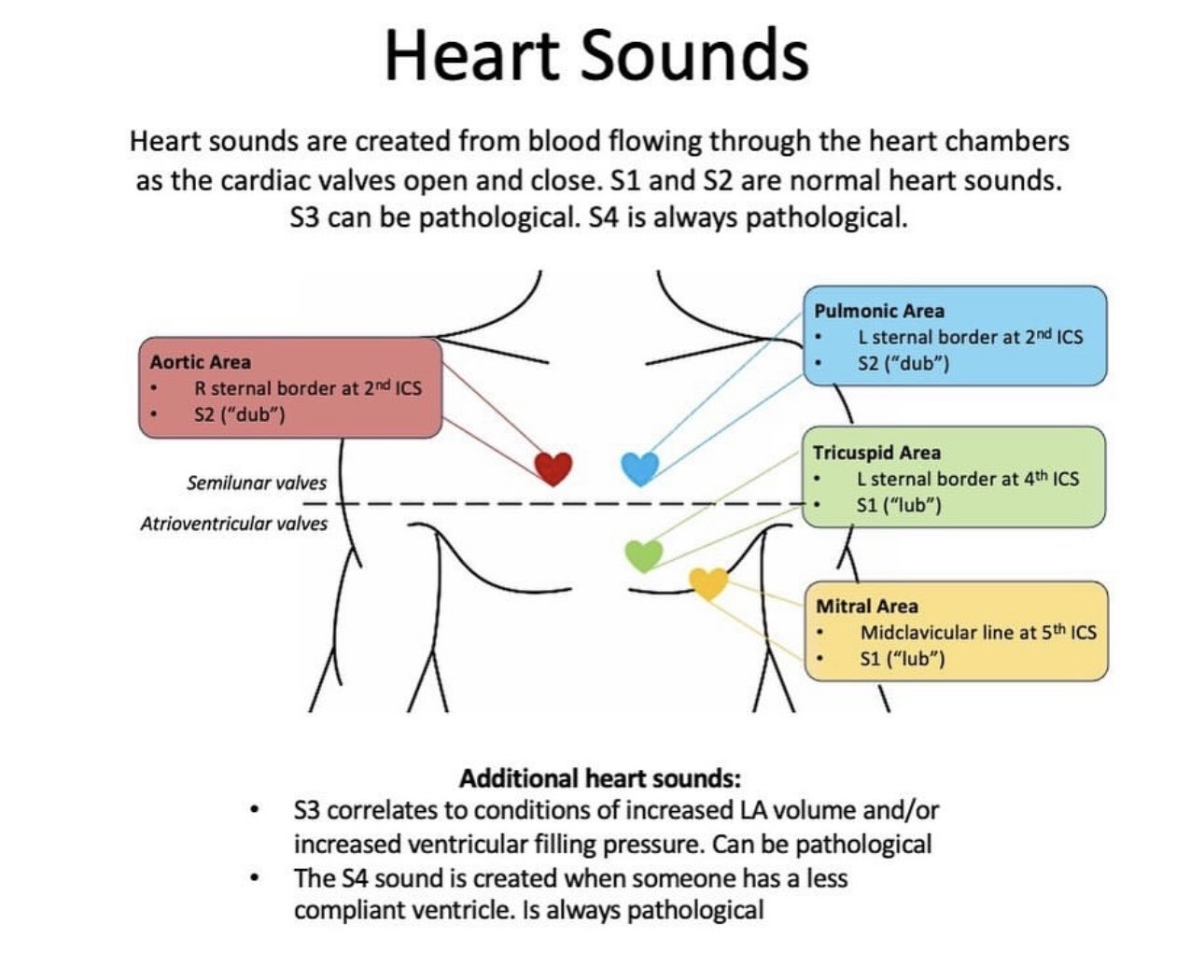
Heart Sounds
| First Heart sound | |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | Caused by closure of mitral and tricuspid valves. |
| Pathology | Loud S1: Usually caused by ventricular systole occurring when the cusps of the mitral valve are far apart and snapped closed by a rapidly rising left ventricular pressure - a bit like a gust of wind catching an open door. Causes the tapping apex beat. Causes: Mitral Stenosis, Hyperdynamic circulation e.g. anaemia, fever, Left to right shunt, Atrial ectopics, Short PR, thin people
Soft S1 Mitral Cusps are close at the time of systole or reduced output. Causes Mitral regurgitation, Severe heart failure, shock, LBBB, Long PR , Aortic stenosis |
| Second Heart sound | |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | Produced by the Aortic valve and then pulmonary valve closing. Louder if shuts more forcefully due to increased pressure gradient e.g. ? BP or fast drop in pressure in ventricle e.g. VSD or MR. Softer if reduced flow e.g. severe aortic stenosis |
| Causes |
|
| Third heart sound | |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | Rapid LV filling into a stiff ventricle but physiological in those under 30 |
| Causes | Sounds like "KENTUCKY" with the S1---PULSE--------- S2--S3 . The causes are Heart failure, Mitral regurgitation, Ventricular septal defect, Dilated cardiomyopathy |
| Fourth Heart sound | |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | Atrial systolic kick produces the sound |
| Causes |
Sounds like "TENNESSEE" with S4 S1 ------PULSE-------S2
|
Prosthetic valves
- Metal Prosthetic sounds - Metal sounds with pulse = Mitral valve After is likely to be aortic.
- Flow murmurs may be heard. Need Warfarin. Longer lasting
- Tissue prosthetic valves - sound normal. Do not need Warfarin. Last shorter. From pig or homograft.
Other findings
- Ejection click - Occur as valves open e.g. aortic and pulmonary and suggest bicuspid valves. May be heard normally in young.
- Mid-systolic click - Seen with Mitral valve prolapse. "click murmur syndrome". May be followed by a PSM.
- Opening snap - as mitral valve opens - associated with mitral stenosis.
- Tumour "plop" - (Left) Atrial myxoma occluding mitral valve orifice in diastole with a loud S1 and MDM which mimics mitral stenosis
Pacemakers
- Usually found in the left infraclavicular fossa and should be easily palpable. Usually, put on the non-dominant side so as not to interfere with limb movement. Might actually be an ICD. Should be an overlying scar.
- An examination to be done in the morgue before you sign a cremation form as unless removed it may explode. Can also look at CXR and ECG to see if the patient has a pacemaker.
- Count the wires - single wire usually a VVI. Two wires are a DDD. More than 2 wires may be an ICD.
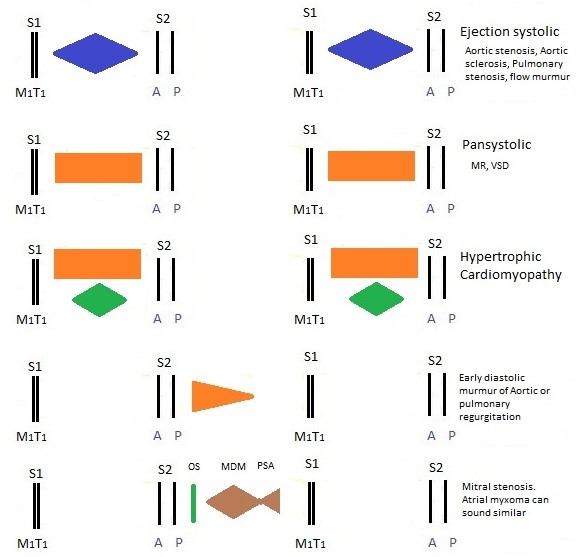
Murmurs
- Murmurs are caused by turbulent inefficient flow so kinetic energy is converted to sound energy.
- They may be due to forward flow through a narrowed valve or backward flow through an abnormally open or incompetent valve.
- Must always time with one finger on the major pulse.
- With the pulse = systolic. Not with pulse = Diastolic.
Detecting murmurs
- Aortic area: 2nd ICS to the right of the sternum
- Pulmonary area: 2nd ICS to the left of the sternum
- Mitral area: At or just medical to the cardiac apex
- Tricuspid: at the lower LSE
Grading of murmurs
- 1. Just audible
- 2. Quiet but audible with stethoscope
- 3. Moderately loud
- 4. Loud
- 5. Heard all over precordium + thrill
- 6. Audible without stethoscope
The five important laws of cardiac auscultation are
- Murmurs with the pulse are systolic, the rest are diastolic
- Right sided murmurs get louder with inspiration and left-sided murmurs louder with expiration
- HCM and Mitral valve prolapse murmurs get louder on standing or Valsalva.
- HCM and MVP murmurs disappear with Squatting and leg raising
- All other murmurs do the opposite to HCM and MVP
- Diastolic murmurs are never innocent and rarely above grade 4
Innocent Murmurs
Diastolic murmurs are never innocent">
- An Innocent murmur is one that is not associated with any underlying heart or systemic disease.
- They are found in children and young adults and during hyperdynamic periods such as fever or pregnancy.
- Some useful pointers can help you differentiate them from murmurs that are associated with underlying problems.
- An innocent murmur is more likely when
- The murmur is soft and systolic
- Heard best at the left sternal edge
- There are no added sounds
- Normal heart sounds
- No thrill, Normal ECG and CXR, No symptoms
Two main types of Innocent murmurs
- Venous hum: Turbulent venous flow around head and neck. Low pitched heard below clavicles. Disappears on lying flat or compression of jugular veins on the same side
- Ejection systolic murmur: Generated in the ventricle, outflow tracts or great vessels. No structural abnormality
Thrill
- A thrill is a palpable murmur and is due to turbulent blood flow and is indicative of a loud murmur.
- The flat of the hand should be placed at the base and apex of the heart.
- A diastolic thrill at the apex is suggestive of severe mitral stenosis (aortic regurgitation rarely produces a thrill).
Parasternal heave
- It is the RV equivalent of the apex beat
- A parasternal heave is a cardiac impulse palpated by placing the flat of the hand on the costal cartilages, to the left of the patient's sternum.
- It may be due to right ventricular hypertrophy when the impulse is at the same time as the apex beat and carotid pulsation.
- Less commonly it is due to left atrial enlargement when the pulsation occurs before the apex beat or carotid pulsation.
Continuous murmur
- Patent Ductus arteriosus
- Coronary AV fistula
- Ruptured sinus of Valsalva
Radiation of murmurs
- Mitral incompetence -> Axilla
- Aortic stenosis -> Carotids and apex
- Aortic incompetence -> Sternal edge
At the end of the examination
- Ask to listen to lung bases for signs of pulmonary oedema
- Ask to look for hepatomegaly and ascites for right heart failure suspected
- Ask to check lower legs - oedema, vein graft scars (sternal scar CABG)
- Offer to examine peripheral pulses