Makindo Medical Notes.com |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER:The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd | |
Related Subjects: |Calcium Physiology |Calcitonin |Hypocalcaemia |Hypercalcaemia |Hypomagnesaemia |Hypermagnesaemia |Primary Hyperparathyroidism |Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia (FHH) |Sarcoidosis
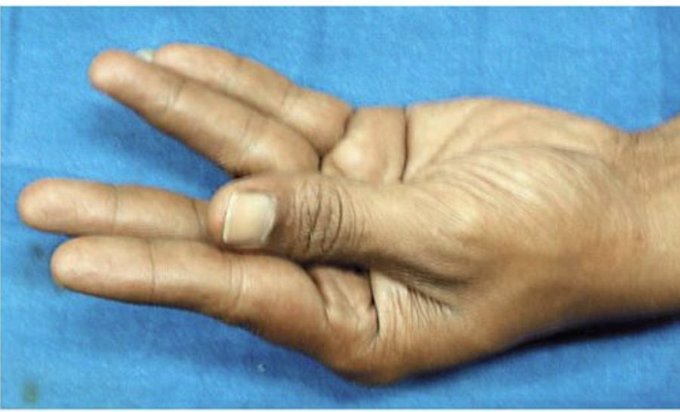
If you find Hypocalcaemia and the cause is not obvious then always look for low magnesium as it causes end-organ resistance to PTH and inhibits the hypocalcaemic feedback loop
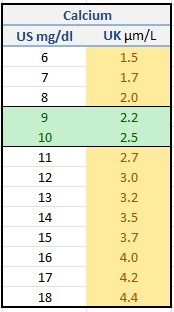
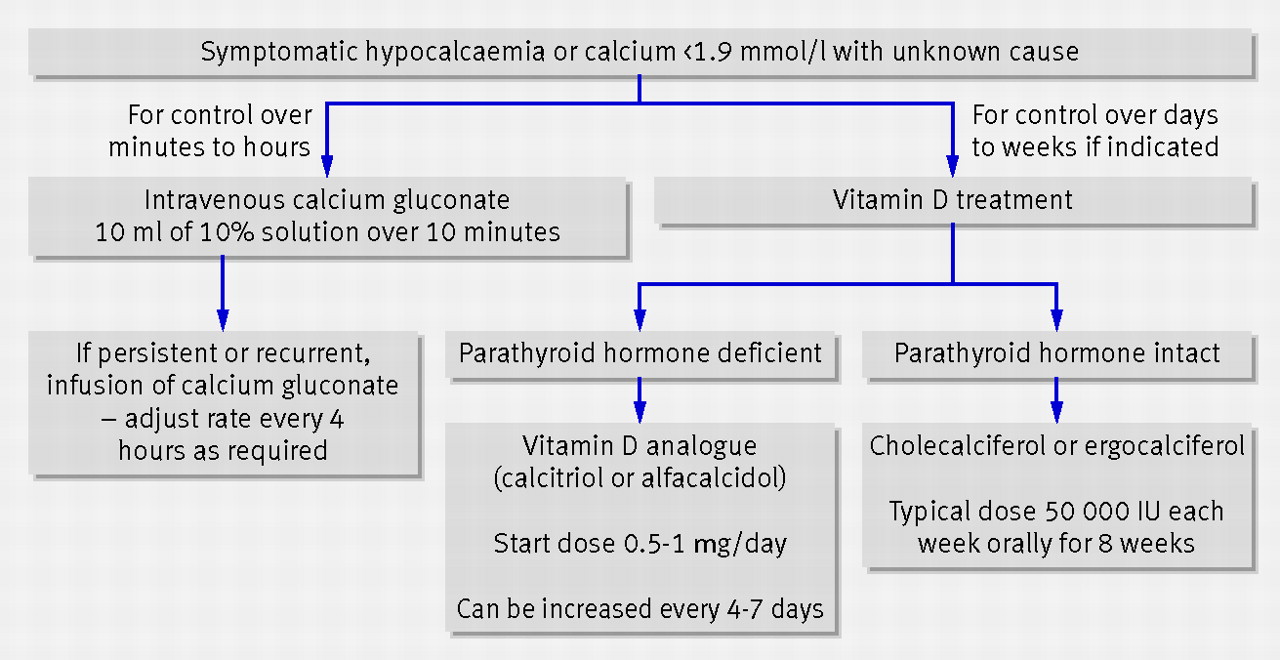
| Severe Hypocalcaemia Management Summary. Are they taking Digoxin ? |
|---|
|
| Cause | Clinical Features | Investigations | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoparathyroidism | Symptoms include tetany, muscle cramps, seizures, numbness, and tingling in the hands, feet, and around the mouth; Chvostek and Trousseau signs may be positive. | Low serum calcium, low PTH levels, elevated serum phosphate, normal or low 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. | Calcium supplementation, vitamin D analogs (e.g., calcitriol), and in some cases, recombinant PTH. |
| Vitamin D Deficiency | Bone pain, muscle weakness, fatigue, and in severe cases, osteomalacia or rickets in children. | Low serum calcium, low 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, elevated PTH, low phosphate levels, low serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels. | Vitamin D supplementation (e.g., cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol), calcium supplementation if needed, and sunlight exposure. |
| Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) | Symptoms may include bone pain, muscle weakness, and signs of secondary hyperparathyroidism due to impaired vitamin D activation and phosphate retention. | Low serum calcium, elevated PTH, elevated serum phosphate, low 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, elevated creatinine, reduced eGFR. | Phosphate binders, active vitamin D analogs (e.g., calcitriol), calcium supplementation, and management of underlying kidney disease. |
| Hypomagnesemia | Muscle cramps, tetany, seizures, arrhythmias, and refractory hypocalcemia, often seen in chronic alcoholism, malnutrition, or malabsorption. | Low serum magnesium, low serum calcium, low or inappropriately normal PTH, normal or low serum potassium. | Magnesium supplementation (oral or IV), correction of calcium levels, and addressing underlying causes of magnesium loss. |
| Acute Pancreatitis | Severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, hypocalcemia due to fat saponification in the inflamed pancreas. | Low serum calcium, elevated serum lipase and amylase, imaging studies showing pancreatic inflammation, signs of systemic inflammation. | Supportive care (IV fluids, pain control), calcium supplementation in severe cases, and treatment of underlying pancreatitis. |
| Pseudohypoparathyroidism | Similar to hypoparathyroidism, with physical features such as short stature, round face, short hand bones, and mental retardation. | Low serum calcium, elevated PTH, low phosphate levels, genetic testing for GNAS mutations. | Calcium supplementation, vitamin D analogs, and management of associated endocrine abnormalities. |
| Sepsis | Systemic signs of infection, hypotension, multi-organ failure, often associated with hypocalcemia due to increased cytokine production and altered calcium metabolism. | Low serum calcium, evidence of infection (e.g., elevated white blood cell count, positive blood cultures), organ function tests. | Treatment of underlying infection with antibiotics, supportive care in ICU, calcium supplementation if severe. |
| Hungry Bone Syndrome | Occurs after parathyroidectomy or thyroidectomy; presents with bone pain, hypocalcemia, and hypophosphatemia due to rapid bone remineralization. | Low serum calcium, low phosphate, low magnesium, elevated alkaline phosphatase, recent history of surgery. | Aggressive calcium supplementation, vitamin D analogs, and monitoring of electrolytes postoperatively. |