Makindo Medical Notes.com |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER:The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd | |
Legionella Pneumophila
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects:
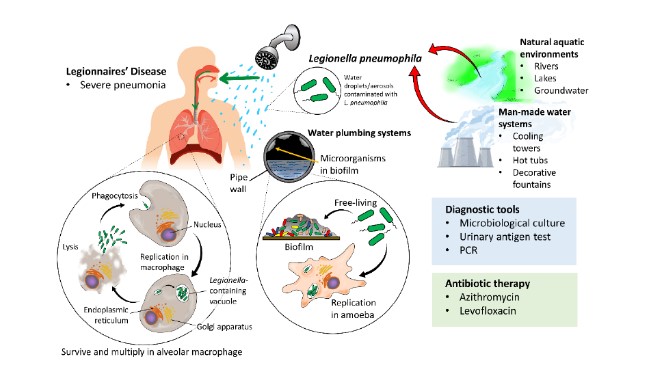
Aquatic organisms found in air conditioning, hot water heaters. Because Legionella is an intracellular pathogen, antibiotics that reach intracellular MICs are most likely to be effective. Large numbers of bacteria can be aerosolized from contaminated water, resulting in epidemic infections, usually in urban setting
Liquid pools in place
Poorly cleaned, drops sprayed at face
Fountains, old AC
Fever, cough, upset GI
Awful CAP, all gone awry
@DrCindyCooper
About
- Outbreak at a American Legion members convention in Philadelphia in 1976
- The attendees acquired pneumonia from an infected air conditioning
- Cause of community-acquired and nosocomial-acquired pneumonia
- Also causes Pontiac fever, a related self-limited upper respiratory tract infection
- Penicillin and Cephalosporins not useful
Characteristics
- Gram negative rod shaped bacilli intracellular
- Obligate aerobes and slow growing Fastidious
- Non motile No capsule. facultative intracellular pathogen
- Infects and replicates within eukaryotic host cells e.g. macrophages
- Adheres to epithelium with fimbriae
- Can survive and even grown within phagocytic cells
- L. pneumophila serogroup 1 (Lp1), the dominant serogroup, accounts for most human infections
Vulnerable patients
- Cardiac, renal, immunologic, or haematologic disease.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or congestive heart failure
- Organ transplant recipients are particularly susceptible.
- Immunosuppressed patients have fatality rates of up to 50%
Source
- Found in water cooler systems growing in water at 20-45 C
- Seen in hotels, hospitals, showers and hot water system
- May grow inside coexisting amoebae. No human-to-human transmission
- Made worse in air conditioning systems by
- lukewarm water temperature
- obstruction and stagnation of water flow
- plumbing materials
- biofilm formation
- Presence of amoeba, which support the growth of Legionella sp.
Clinical: GI symptoms are a clue
- Muscle aches, tiredness, headaches, dry cough and fever.
- Sometimes diarrhoea occurs and confusion may develop
- Atypical pneumonia which can be severe and necrotising
- Non-productive cough, Flu-like symptoms - "Pontiac fever"
- Seen in diabetics, immunosuppressed, smokers, alcoholism
Investigations
- FBC, U&E, LFTs, CRP. CXR. ECG
- Culture and grows on Buffered Charcoal Yeast Extract [BCYE] agar plus antibiotics media but takes 3-5 days
- Legionella serology and/or Legionella urine antigen testing
- Legionella pneumophila polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Management
- ABC, Oxygen, HDU/ITU as needed. IV fluids.
- Antibiotics: 10-21 days of antibiotics such as Erythromycin or Azithromycin, clarithromycin, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin and doxycycline are excellent choices. Tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, and other fluoroquinolone and macrolide drugs may be indicated.
- If your patient has Pontiac fever, antibiotic treatment should not be prescribed. It is a self-limited illness that does not benefit from antibiotic treatment. Patients usually recover within 1 week.
- Prevent with hyperchlorination, water > 70 C