Makindo Medical Notes.com |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER:The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd | |
Related Subjects:
|Olfactory Nerve
|Optic Nerve
|Oculomotor Nerve
|Trochlear Nerve
|Trigeminal Nerve
|Abducent Nerve
|Facial Nerve
|Vestibulocochlear Nerve
|Glossopharyngeal Nerve
|Vagus Nerve
|Accessory Nerve
|Hypoglossal Nerve
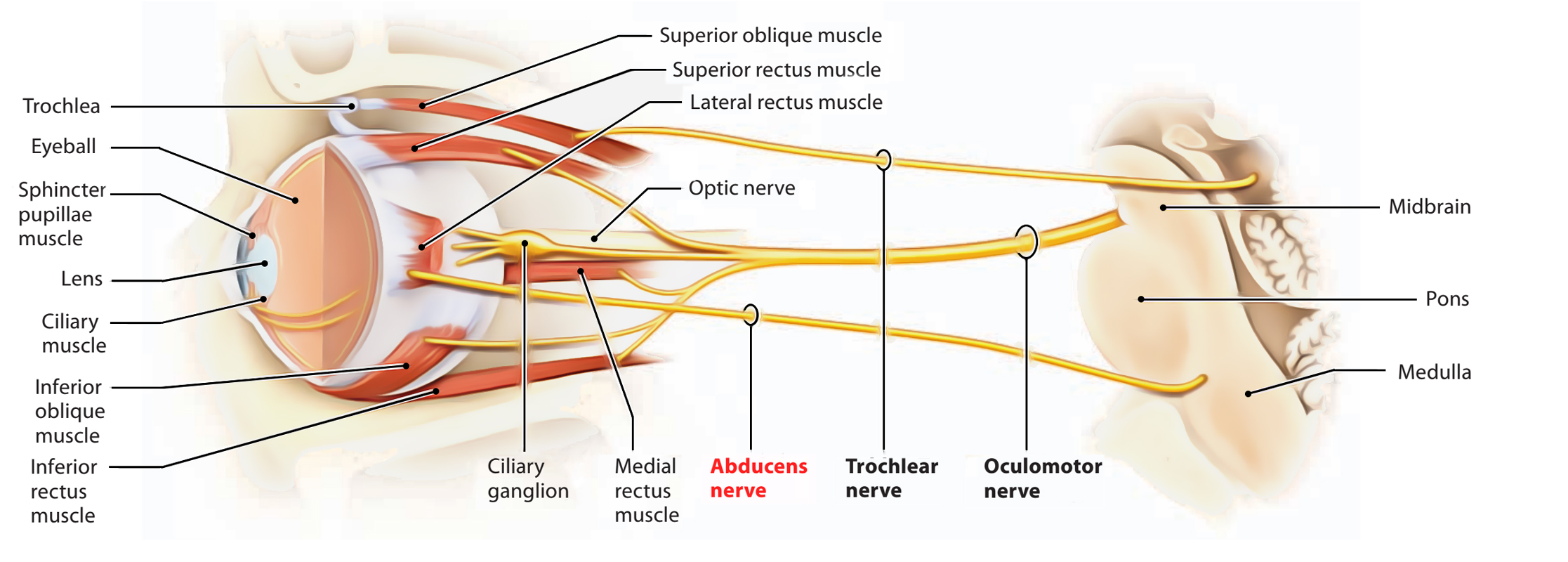
The oculomotor nerve, also known as cranial nerve III, is responsible for most of the eye's movements, including the constriction of the pupil and maintaining an open eyelid.
The oculomotor nerve is essential for eye movements, pupil constriction, and maintaining an open eyelid. It arises from the midbrain and innervates several muscles involved in these functions. Damage to the oculomotor nerve can lead to conditions such as oculomotor nerve palsy and Horner's syndrome, which require appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Oculomotor Nerve (Cranial Nerve III)
Anatomy of the Oculomotor Nerve
Functions of the Oculomotor Nerve
Clinical Relevance
Summary
