Makindo Medical Notes.com |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER:The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd | |
Wilson disease
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Chronic liver disease |Cirrhosis |Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) |Liver Function Tests |Ascites Assessment and Management |Budd-Chiari syndrome |Autoimmune Hepatitis |Primary Biliary Cirrhosis |Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis |Wilson disease |Hereditary Haemochromatosis |Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency |Non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) |Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis |Alcoholism and Alcoholic Liver Disease
Wilson's disease accounts for 6-12% of all patients with acute liver failure who are referred for emergency transplantation. Wilson's disease should be considered in any individual with liver abnormalities or neurological movement disorders of uncertain cause. Age alone should not be the basis for eliminating a diagnosis of Wilson's disease
About
- Autosomal recessive disorder of copper transport.
- Occurrence is in 1 in 30,000 live births.
- Untreated leads to cirrhosis and neurological problems.
- Early diagnosis is fundamental as early treatment is important.
Aetiology
- There is a mutation in the ATP7B gene on chromosome 13 seen in 1 in 90.
- Over 200 mutations in the ATP7B gene have been reported.
- This encodes a copper carrying ATPase. There are several different mutations.
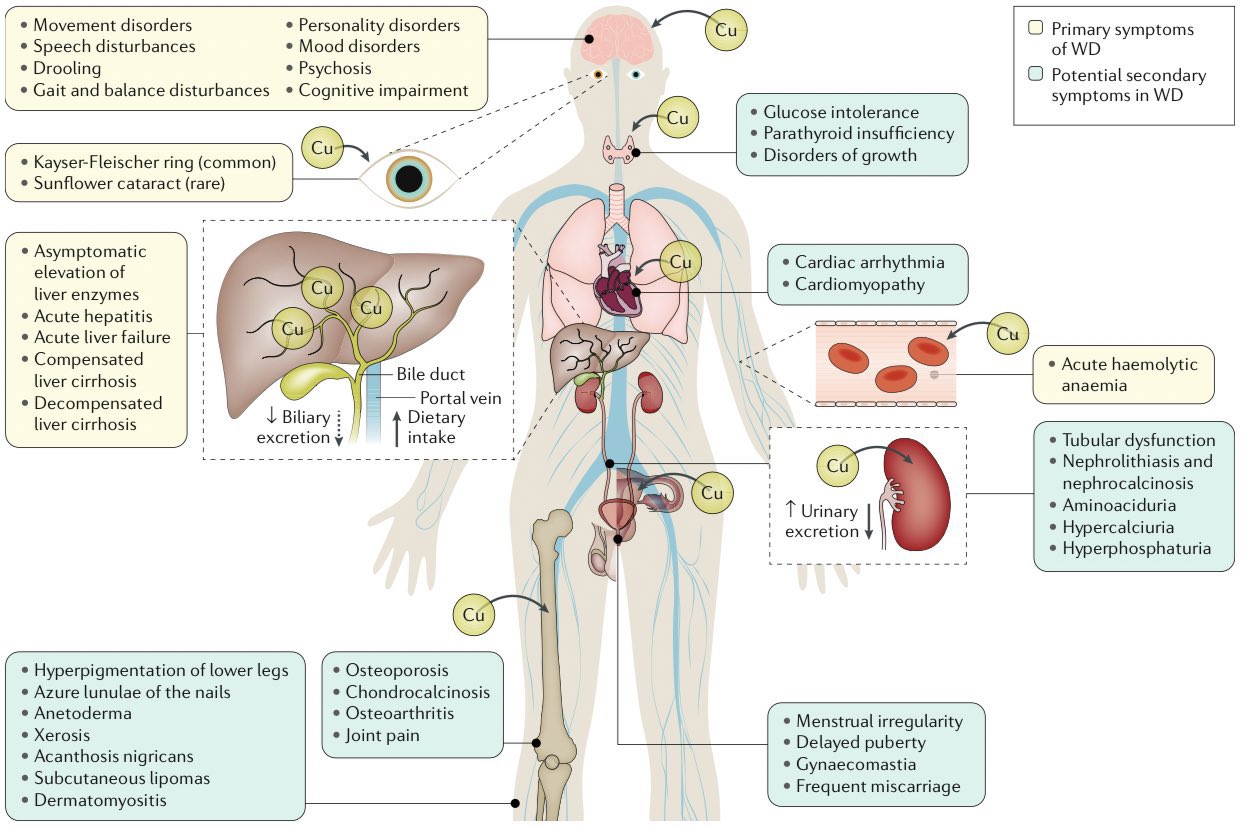
- Action of Copper transporting ATPAse is to excrete hepatic copper into biliary tree
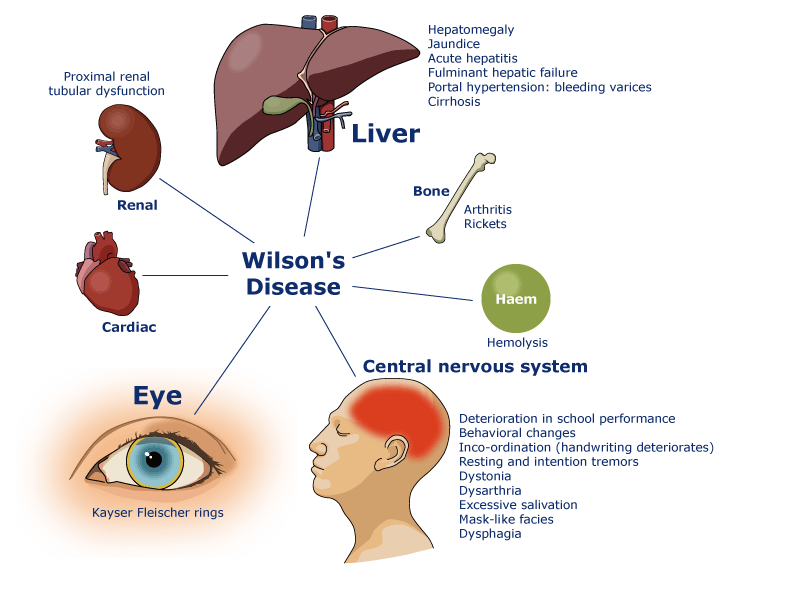
Kayser-Fleischer rings caused by deposition of copper in Descemet's membrane of the cornea. They are not entirely specific for Wilson's disease
Clinical
- Symptoms can begin between ages of 5 and 45
- Neurological and psychiatric symptoms commoner in young
- Kayser-Fleischer rings best seen with slit lamp examination at 12 O'Clock at the corneal/scleral margin and resolve with treatment. There is copper deposition in Descemet's membrane.
- Anaemia and Jaundice from haemolysis and Cirrhosis - Excess free copper causes oxidative damage of red cell membrane.
- Sunflower cataract on posterior surface of lens
- Acute or Chronic Hepatitis and eventual cirrhosis, hepatosplenomegaly and jaundice
- Dysarthria, dystonia, rigidity, tremor
- Choreoathetosis due to basal ganglia deposition
- Titubation and a wing beating tremor
- Psychiatric - irritability, anger, poor self control
- Osteoporosis and rickets
Manifestation of Wilson disease
Investigations
- Elevated Liver transaminases
- Prolonged Prothrombin time in advanced liver disease
- Evidence of a Coombs negative haemolytic anaemia
- Low serum caeruloplasmin level < 0.2 g/L)
- Serum Free copper > 1.6 micromol/L
- High urine copper >1.6 micromols/24 h
- 24-hr urinary copper excretion > 1.6 micromoles/24 hrs (normal <30 µg) but need to use copper free containers
- Increased Hepatic copper content (>250 mcg/kg of dry weight) (normal is 20-50 mcg)
- Urine - Renal tubular defect - proteinuria, glycosuria
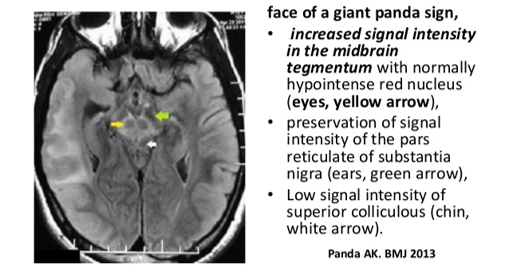
- MRI: basal ganglia and cerebellar changes with giant panda sign
- Genetic testing : can be useful but more than 500 mutations
Haemolysis
The combination of Kayser-Fleischer rings and a low serum ceruloplasmin (<0.1 g/L) level is sufficient to establish a diagnosis.
Management
- Untreated Wilson's disease is universally fatal, with most patients dying from liver or neurological disease and chelation treatment and liver transplantation has led to prolonged survival
- Copper chelation therapy with D-Penicillamine (Side effects - Lupus like syndromes and nephrotic syndrome) + Pyridoxine to avoid any deficiency
- Dietary restriction of copper
- Oral Zinc acetate - blocks GI Copper uptake and very safe and non-toxic
- Triethylene tetramine dihydrochloride
- Liver Transplantation is curative