Related Subjects:
|Calcium Physiology
|Bisphosphonates
|Osteoporosis
|Osteonecrosis of the jaw
The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of osteoporosis has been widely adopted and is based on the measurement of BMD, with reference to the number of SDs from the BMD in an average 25-year-old woman (T-score):
About
- Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterised by decreased bone mass and deterioration of bony microarchitecture
- In practice it is diagnosed in those with a T score < 2.5 SD or fragility fractures in those at risk
- Can be due to age or other diseases or drugs
Classification
- Normal: T-score of -1 SD or more
- Osteopenia : T-score between -1 and -2.5 SD
- Osteoporosis : T-score < -2.5 SD
- Established osteoporosis : T-score < -2.5 SD + associated fragility fracture(s).
Causes of non Age related Osteoporosis
- Smoking
- Parental history,
- Alcohol >4 units daily
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Low BMI <19
- Prolonged immobility
- Untreated menopause.
- Steroid use of >5mg/d of prednisolone.
- Hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, hypercalciuria.
- Low Testosterone (treatment of ca prostate).
- Early menopause.
- Renal or liver failure.
- Erosive/inflammatory bone disease (eg myeloma or rheumatoid arthritis).
- Dietary low Ca²⁺/malabsorption
- Diabetes mellitus type 1.
Clinical
- Possibly clinically and biochemically silent until fracture
- Vertebral fractures: Back pain, Loss of height, Kyphosis
- Appearance of abdominal swelling as the collapse of lumbar vertebrae
- Other fractures: Neck of Femur, Colles, Humerus
Risk factors for Osteoporosis
- Female, Increasing Age, Caucasian, Smoking
- Low exposure to Oestrogen - late menarche and early menopause
- Malabsorption - Coeliac, Steroid usage - COPD,Cushing syndrome
- Hyperthyroidism, Hyperparathyroidism, Family history of osteoporosis
- Alcoholism, Chronic Heparin injection, Methotrexate ?, Diabetes mellitus
- Immobilisation, Gaucher's disease, Myeloma, Mastocytosis
- Obesity is not a risk factor
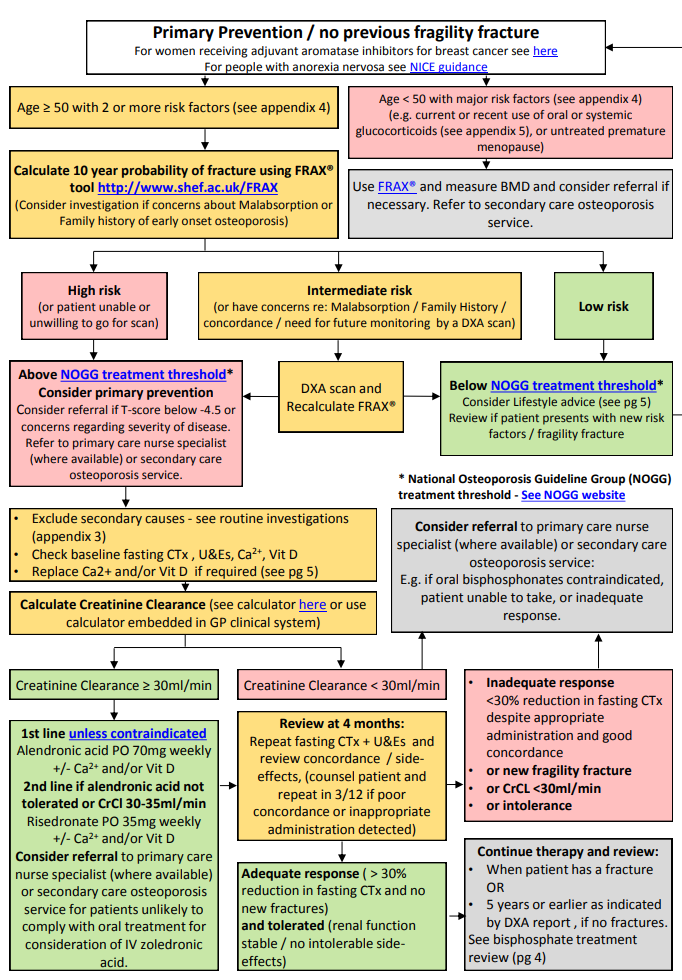
Investigations
- FBC, ESR/CRP, U&E, Ca, P, ALP, AST, Albumin, TFT
- X-ray: not helpful
- X ray of Fragility fracture: Investigate for metastatic bone cancer, myeloma, osteomalacia, Paget's disease
- Bone biopsy - not practical
- DEXA scan: Use Hip rather than spine. Bone mineral density (g/cm2)
is compared with young healthy adult. The score is the number of
standard deviations the bone mineral density (BMD) is from the youthful
average. Each decrease of 1 SD in BMD increases x2.6-fold in risk of hip fracture. It is not needed in older females with clear evidence of osteoporosis
- -1 to -2.5: Osteopenia. Risk of fracture. Off er lifestyle advice.
- -2.5 or lower: Osteoporosis. Lifestyle advice and treatment. Repeat
DEXA in 2yrs.
- Look for underlying cause in a younger person
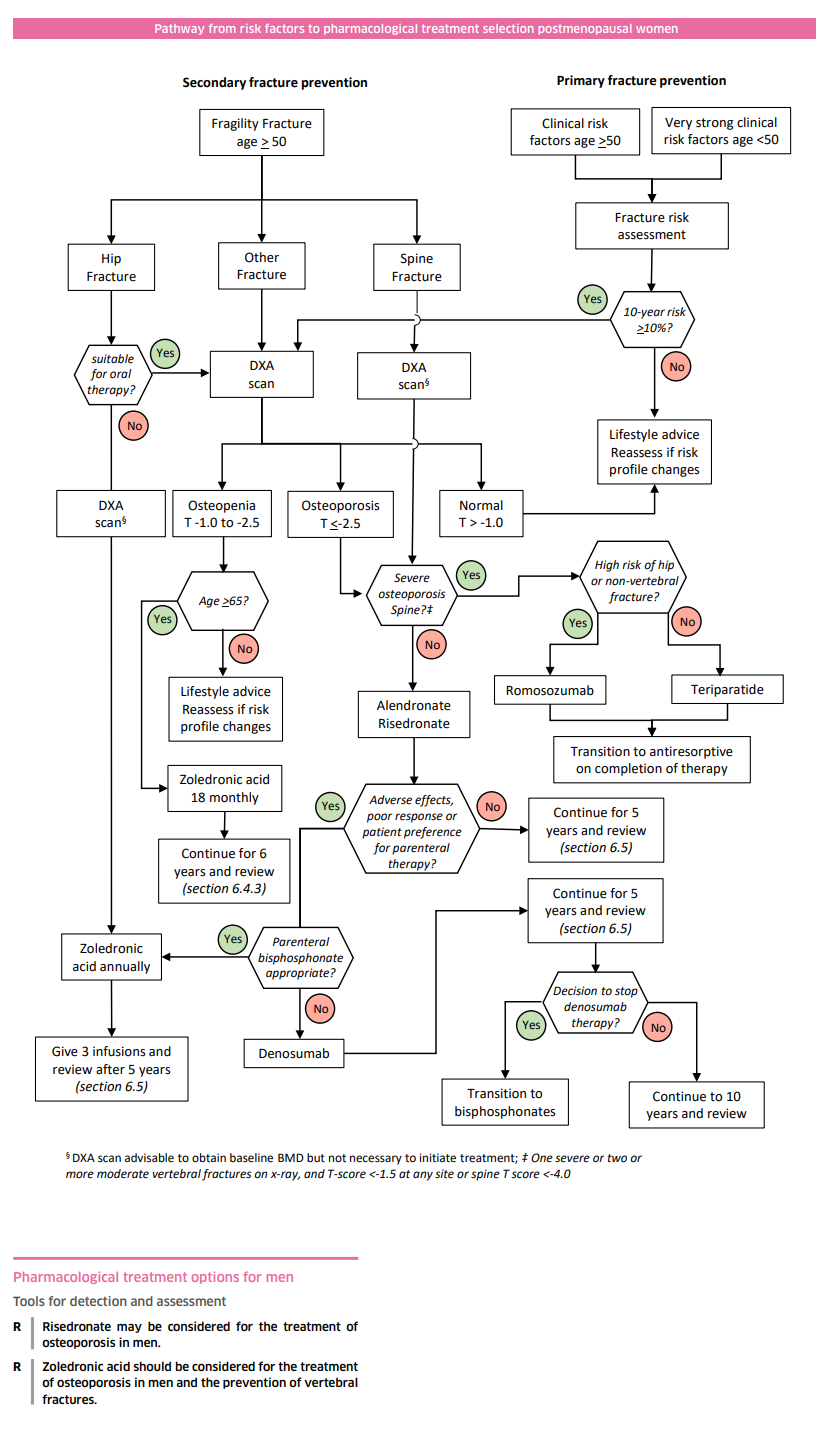
Management
- General: Smoking. Avoid excess Alcohol. Weight bearing exercise. Balance exercises. Ca/Vit D rich diet. Home fall risk prevention.
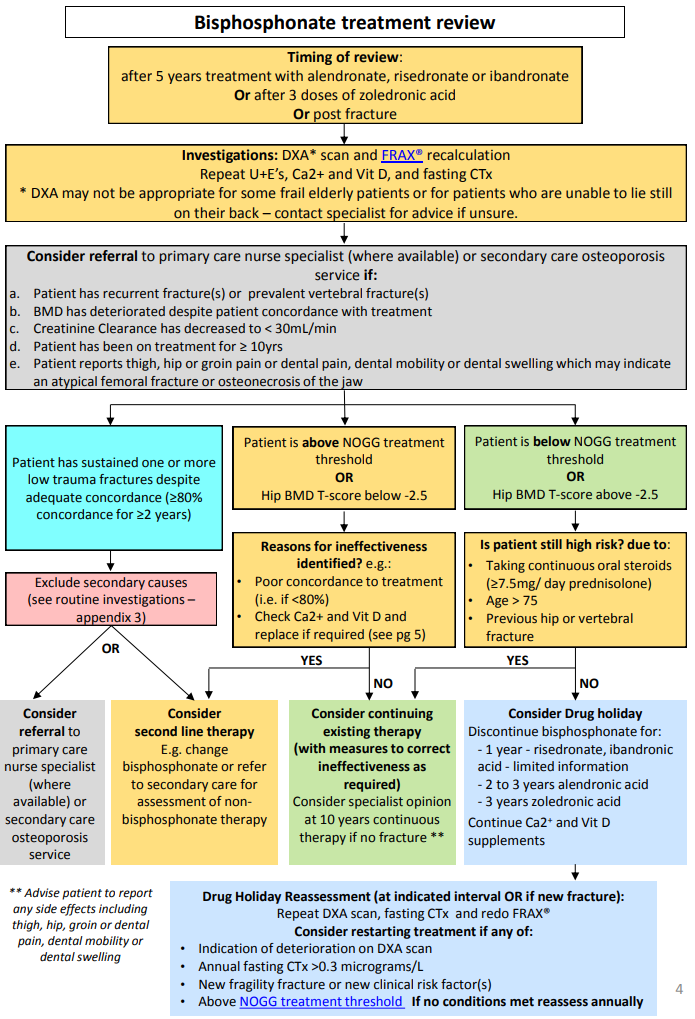
- Bisphosphonates
- Alendronate 10 mg OD or 70 mg Weekly or Risedronate sodium 5mg OD or 35mg once weekly.
- These drugs increase BMD and reduce hip and vertebral fractures and reduce fractures by about 50% in the postmenopausal OP. Given daily or weekly. They require that patient can sit up/stand and has no problems swallowing.
- Calcium and vitamin D: Give calcium 1g/d + vit D 800U/d. Target serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D level 0.75nmol/L.
- Denosumab 60mg subcutaneous injection every 6 months. It is a monoclonal Ab to RANK ligand. Reduces resorption.
- Strontium ranelate stimulates bone growth and reduce bone resorption. Strontium ranelate 2g /sachet.
- Raloxifene is a selective oestrogen receptor modulator. It reduces bone resorption by osteoclasts. Side effects - hot flushes, VTE, muscle cramps, reduces breast cancer. No effect on stroke or heart disease. No evidence of benefit on non-vertebral fractures.
- Teriparatide: a recombinant form of parathyroid hormone, used in the treatment of advanced osteoporosis. Usually in those with a very high risk of fracture and T score less than -4 SD. Teriparatide 20mcg daily by subcutaneous injection (max. duration 18 months, not to be repeated)
- Testosterone may help in hypo gonadal men by promoting trabecular connectivity
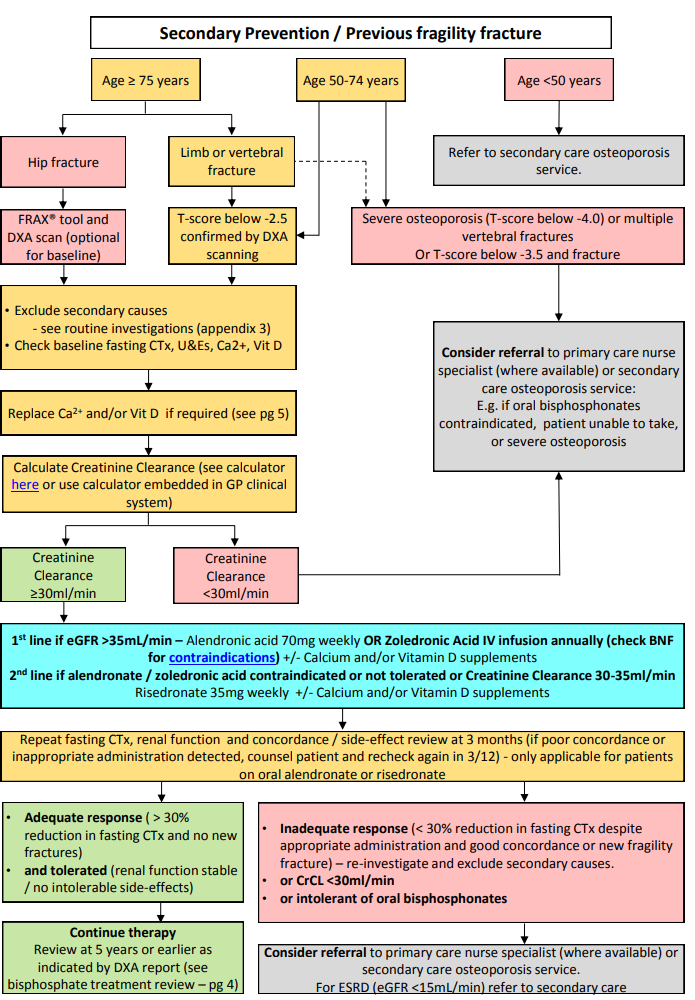
Management of Steroid induced Osteoporosis
- At risk are those taking more than Prednisolone 7.5mg a day for 3 or more months
- Patients over the age of 65 years or those who've previously had a fragility fracture should be offered bone protection.
- Patients under the age of 65 years should be offered a bone density scan, with further management dependent on Dexa scan T score. The first-line treatment is alendronate. Patients should also be calcium and vitamin D replete
- Greater than 0 Reassure
- Between 0 and -1.5 Repeat bone density scan in 1-3 years
- Less than -1.5 Offer bone protection
SIGN Guidance
Primary Prevention
Secondary Prevention
Bisphosphonates
References



