Makindo Medical Notes.com |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER:The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd | |
Related Subjects: |Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia (FHH) |Primary Hyperparathyroidism |Lung Cancer |Hypercalcaemia |Multiple Myeloma |Oncological emergencies |Bisphosphonates
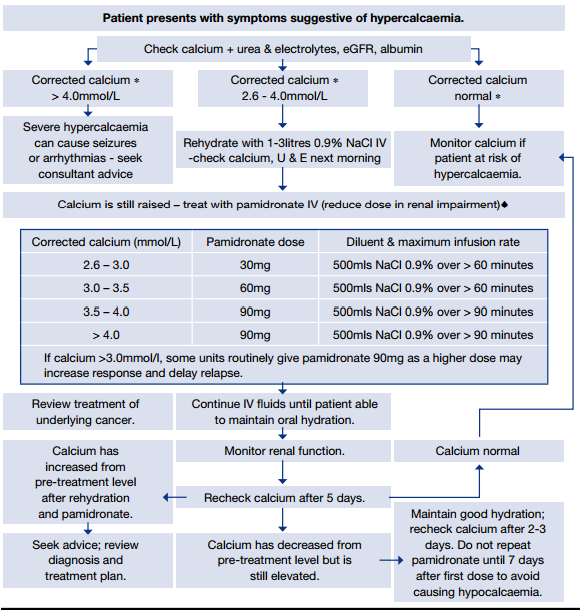
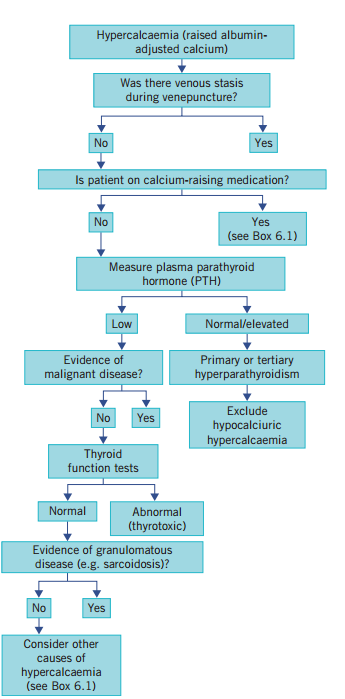
An albumin adjusted serum calcium of over 2.6 mmol/L (UK). More than 90% of cases are due to malignancy or primary hyperparathyroidism
| Initial Hypercalcaemia: Total serum calcium > 10.5 mg/dL (2.6 mmol/L). |
|---|
|
| Cause | Clinical Features | Investigations | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Hyperparathyroidism | Often asymptomatic; can present with bone pain, fractures, nephrolithiasis, polyuria, constipation, and mental disturbances ("stones, bones, abdominal groans, and psychiatric overtones"). | Elevated serum calcium, elevated or inappropriately normal PTH levels, low serum phosphate, 24-hour urinary calcium excretion. | Surgical removal of the overactive parathyroid gland(s), hydration, bisphosphonates for bone protection, monitoring in mild cases. |
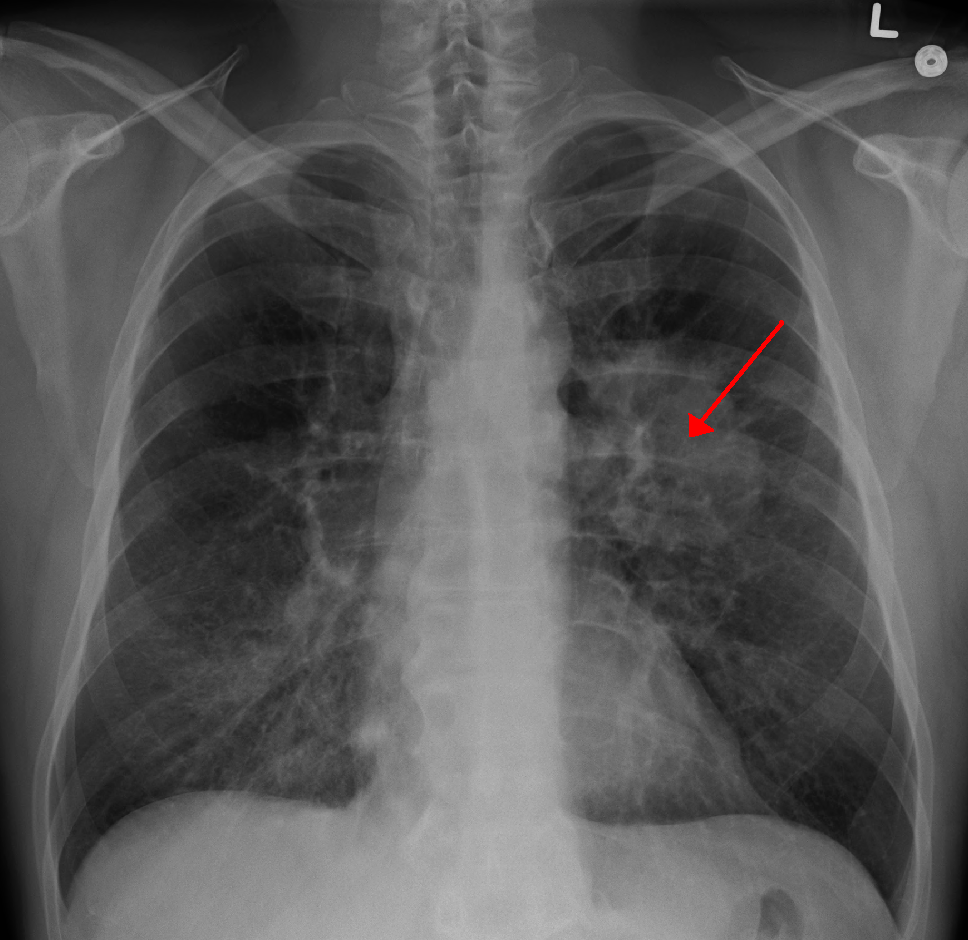
| Malignancy-Associated Hypercalcemia | Symptoms of advanced malignancy, such as weight loss, fatigue, bone pain, polyuria, dehydration, and confusion; may be related to PTHrP-secreting tumours or osteolytic metastases. | Elevated serum calcium, suppressed PTH, elevated PTHrP in cases of humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy, imaging studies to identify primary tumour or metastases. | Intravenous fluids, bisphosphonates, denosumab, treatment of the underlying malignancy, corticosteroids in certain cases. |
| Vitamin D Toxicity | Hypercalcemia with symptoms like nausea, vomiting, polyuria, dehydration, and confusion, usually related to excessive vitamin D or calcium intake. | Elevated serum calcium, elevated 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, suppressed PTH, normal or elevated serum phosphate. | Discontinue vitamin D and calcium supplements, hydration, corticosteroids, and bisphosphonates in severe cases. |
| Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Diseases | Fatigue, weight loss, polyuria, hypercalcemia-related symptoms; may also present with symptoms of the underlying disease such as respiratory issues in sarcoidosis. | Elevated serum calcium, elevated 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels, suppressed PTH, imaging and biopsy for granulomas. | Corticosteroids to reduce granuloma formation, hydration, and bisphosphonates in severe cases. |
| Thiazide Diuretics | Thiazide-induced hypercalcemia typically presents with mild, asymptomatic hypercalcemia; may exacerbate underlying hyperparathyroidism. | Elevated serum calcium, suppressed PTH, history of thiazide use, exclusion of other causes. | Discontinuation of thiazide diuretics, monitoring serum calcium levels, and treatment of any underlying conditions. |
| Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia (FHH) | Mild hypercalcemia, often asymptomatic, with a family history of hypercalcemia; typically presents in childhood or early adulthood. | Elevated serum calcium, low urinary calcium excretion, genetic testing for mutations in the CASR gene, normal or mildly elevated PTH. | No treatment required, as this condition is usually benign; genetic counseling may be offered. |
| Immobilization | Hypercalcemia typically occurs in patients with prolonged immobilization, especially those with high bone turnover (e.g., Paget's disease, adolescents). | Elevated serum calcium, normal or suppressed PTH, history of prolonged immobilization, elevated bone turnover markers. | Increased mobility if possible, bisphosphonates to reduce bone resorption, hydration. |
| Hyperthyroidism | Symptoms of hyperthyroidism such as weight loss, tachycardia, heat intolerance, along with mild hypercalcemia. | Elevated serum calcium, suppressed PTH, elevated thyroid hormones (T3, T4), suppressed TSH. | Treatment of hyperthyroidism (e.g., antithyroid drugs, radioactive iodine), hydration, bisphosphonates if hypercalcemia is severe. |