Makindo Medical Notes.com |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER:The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd | |
Assessing a Patient who is Shocked
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: Atropine |Acute Anaphylaxis |Basic Life Support |Advanced Life Support |Adrenaline/Epinephrine |Acute Hypotension |Cardiogenic shock |Distributive Shock |Hypovolaemic or Haemorrhagic Shock |Obstructive Shock |Septic Shock and Sepsis |Shock (General Assessment) |Toxic Shock Syndrome |Respiratory Failure |Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) |Intubation and Mechanical Ventilation |Critical illness neuromuscular weakness |Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome
A patient with a palpable radial pulse indicates a SBP of at least 80 mmHg, and a palpable femoral pulse indicates SBP of at least 70 mmHg.
| Initial Shock Management: Oxygen 15 L/min unless COPD. NS= N-Saline |
|---|
|
Shock’ exists when oxygen delivery fails to meet the metabolic requirements of the tissues. Shock is not equal to hypotension, but hypotension may be a late manifestation of circulatory failure with failure to deliver oxygen to tissues
Introduction
- Acute circulatory collapse with evidence of insufficient end-organ perfusion.
- There are multiple causes of shock which affect the onset and presentation.
- Shock is due to low Cardiac output or a loss of Systemic vascular resistance or both
Clinical features of shock
- Tachypnoea: Rapid, shallow respiration
- Tachycardia (> 100/min)
- Hypotension (systolic BP < 100 mmHg)
- Drowsiness, confusion, irritability
- Oliguria (urine output <0.5 mL/hr/kg)
- Multi-organ failure
- Vasodilated shock: Warm peripheries, Low diastolic BP
- Hypovolaemic shock: Cold, clammy skin
Classification
- Cardiogenic: MI, Myocarditis, Endocarditis
- Obstructive: PE , Tamponade, tension PTX
- Septic: Uro/Chest/Abdominal other
- Anaphylactic: bee sting, nuts
- Hypovolaemic/Haemorrhagic: GI bleed, Trauma
- Neurogenic: spinal injury
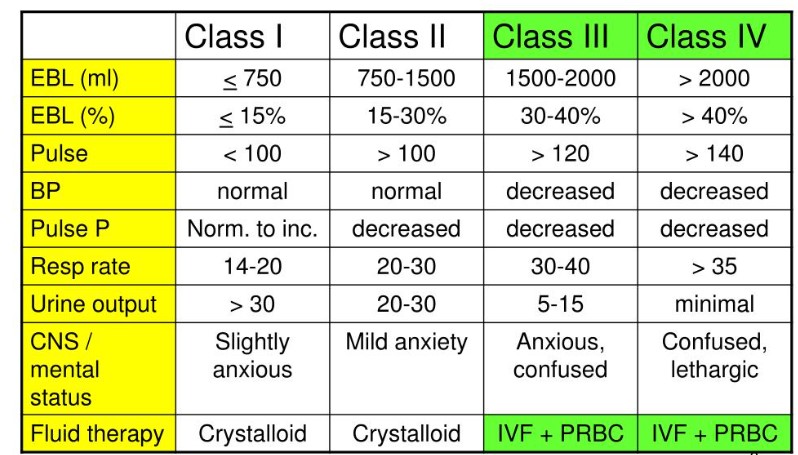
Severity
Clinical Indicators of possible aetiology
- Chest pain: MI (cardiogenic shock or acute MR), Aortic dissection, PE
- Breathless, Cyanosis: LVF, Pneumothorax and tamponade, Acute severe asthma
- Haemoptysis, Melena: GI bleed needs endoscopy
- Pelvic or femur fracture: local bleed or fat embolism or PE
- Fever, malaise, cough, sputum, low neutrophils, immunocompromised: Sepsis
- Abdominal pain: Perforation and sepsis, Leaking AAA
- Severe breathless with Ketones on the breath: DKA needs fluids/potassium and Insulin
- Pregnancy and abdominal pain: Ectopic pregnancy. check beta-HCG get USS
- Retained Tampon: Toxic shock syndrome
- Recent immobility: PE needs anticoagulation
- Pigmented: Addison's disease. Low Na, High K needs steroids
- Non-blanching rash: Meningococcal septicaemia needs Antibiotics
Investigations
- FBC: elevated or low WCC with sepsis. Low HB with bleed
- U&E: often AKI
- Glucose; High with DKA, HHS
- Lactate often elevated
- Troponin elevated in MI
- Dimer elevated in PE
- CXR: consolidation and sepsis, widened mediastinum in aortic dissection, LVF
- Cortisol: Addison (treat if suspicious as the diagnosis can be made later)
Management
- ABC, Get good Venous access
- Treat likely cause and get expert advice early