Makindo Medical Notes.com |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER:The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd | |
Glycolysis Krebs Electron Transport Chain
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects:
|Fat Metabolism
|Glucose Metabolism
|Protein metabolism
|Glycolysis_Krebs_Electron_Transport_Chain
Glycolysis in Cell Cytoplasm
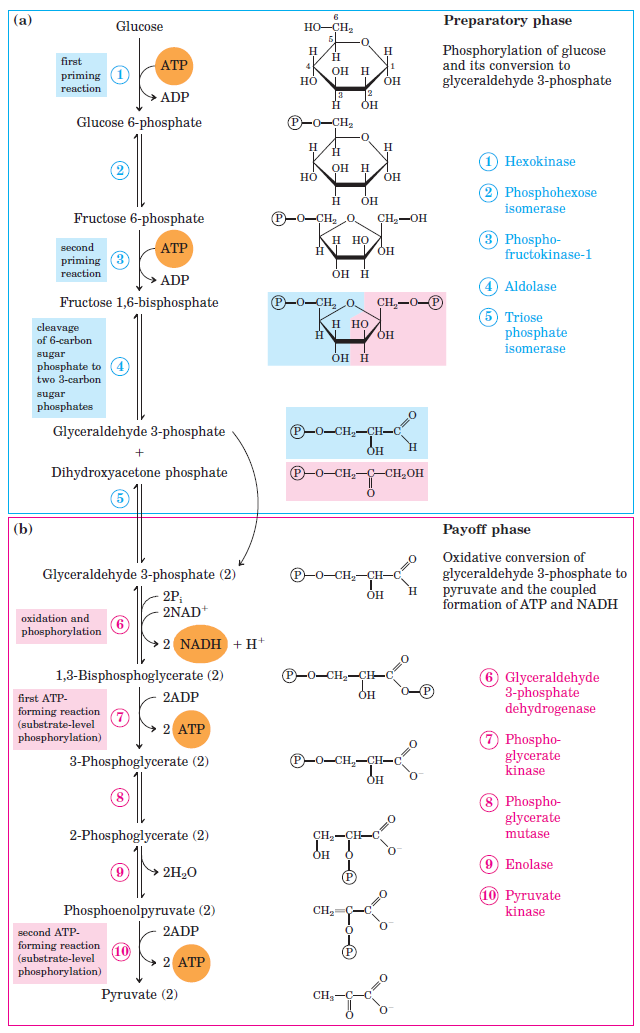
Control
Krebs in Mitochondria
About
Kreb's cycle (2-10)
Functions of Kreb's cycle are
Generation of high energy intermediaries for the next stage of oxidative phosphorylation